Many electric car owners suffer terribly when experiencing cold weather, which also dissuades many consumers who are hesitant to give up fuel vehicles to choose electric vehicles.
Although we all admit that in the cold season, fuel vehicles will also have similar effects – decreased range, increased fuel consumption, and long periods of extremely low temperature may cause the vehicle to fail to start. However, the long-range advantage of fuel vehicles overshadows these negative effects to some extent.
In addition, unlike the engine of a fuel car, which generates a large amount of waste heat to warm the cabin, the efficient operation of the electric motor of an electric vehicle generates almost no waste heat. Therefore, when the ambient temperature is low, the latter needs to consume additional energy to heat for comfortable driving. This also means more loss of EV range.
We worry because of the unknown. If we have enough knowledge about electric vehicles and understand how to exploit their strengths and avoid their weaknesses so that they can serve us better, then we don’t have to worry anymore. We can embrace it more actively.
Now, let’s discuss how cold weather affects the Range and Charging of EVs, and what effective methods we can use to weaken these effects.
Actionable Insights
We tried to come up with some solutions from the perspective of a charging equipment supplier that can reduce the negative impact of cold weather.
- First, do not let the electric vehicle’s battery level drop below 20%;
- Pre-treat the battery with heating before charging, use seat and steering wheel warmers, and lower cabin heating temperature to reduce energy consumption;
- Try to charge during the warmer periods of the day;
- Preferably charge in a warmer, enclosed garage with the maximum charging set to 70%-80%;
- Use plug-in parking so the car can draw energy from the charger for heating instead of consuming the battery;
- Drive with extra caution on icy roads, as you may need to brake more frequently. Consider disabling regenerative braking, certainly, this depends on the specific vehicle and driving conditions;
- Charge immediately after parking to reduce battery preheating time.
Some Things to Know Beforehand
EV battery packs provide power through chemical reactions. The activity of this electrochemical reaction, which occurs at the positive and negative electrode/electrolyte interface is related to the temperature.
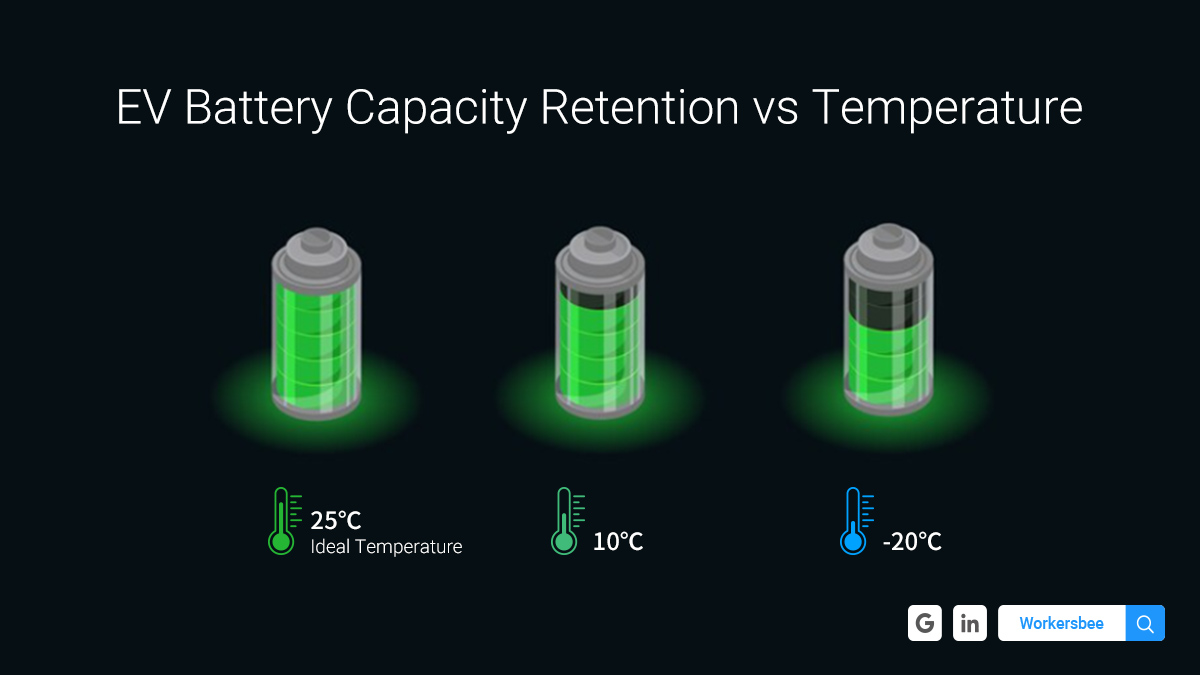
Chemical reactions run faster in warmer environments. The low temperature increases the viscosity of the electrolyte, slows down the reaction in the battery, increases the internal resistance of the battery, and makes the charge transfer slower. The electrochemical polarization reaction is intensified, the charge distribution is more uneven, and the formation of lithium dendrites is promoted. This means that the effective energy of the battery will be reduced, which means the range will be reduced. Low temperatures also impact fuel cars, but electric cars are more obvious.
Even though it is known that low temperatures cause a loss in the cruising range of EVs, there are still differences among different vehicles. According to market survey statistics, battery capacity retention will decrease by 10% to 40% on average at low temperatures. It depends on the car model, how cold the weather is, the heating system, and factors such as driving and charging habits.
When the battery temperature of an EV is too low, it cannot be charged effectively. Electric cars will first use the input energy to heat the battery and only start actual charging when it reaches a certain temperature.
For EV owners, cold weather means a lower range and longer charging time. Therefore, experienced ones usually charge overnight during the cold season and preheat the car before setting off.
Thermal Management Technology for EVs
Thermal management technology of electric vehicles is critical to battery performance, range, and driving experience.
The primary task is to manage the battery temperature so that the battery can work or charge within the appropriate temperature range and maintain excellent working conditions. Ensure battery performance, life, and safety, and effectively extend the range of electric vehicles in winter or summer.
Secondly, to improve the driving experience, effective thermal management will provide drivers with a more comfortable cabin temperature in hot summers and cold winters, reduce energy loss, and improve energy efficiency.
Through the effective allocation of the thermal management system, the heat and cooling needs of each circuit are balanced, thereby reducing energy consumption.
Current mainstream thermal management technologies include PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) which relies on resistance electric heaters and Heat Pump technology that utilizes thermodynamic cycles. The development of these technologies is of great significance to improving the performance, safety, energy efficiency, and driving experience.
How Cold Weather Affects EV Range
At this point, everyone has a consensus that cold weather will reduce the range of electric vehicles.
However, there are two types of loss in the EV range. One is Temporary Range Loss, which is a temporary loss caused by factors such as temperature, terrain, and tire pressure. Once the temperature warms back to the right temperature, the lost mileage will come back.
The other is Permanent Range Loss. Vehicle age (battery life), daily charging habits, and daily maintenance behaviors will all cause vehicle range loss, and they may not revert.
As mentioned above, cold weather will reduce the performance of EV batteries. It will not only reduce the activity of chemical reactions in the battery and reduce the retention of battery capacity but also reduce the charging and discharging efficiency of the battery. The battery’s resistance increases and its energy recovery capability decreases.
Unlike fuel cars, electric cars must consume their battery energy and generate heat to warm the cabin and heat the battery, which increases energy consumption per mile and reduces range. At this time, the loss is temporary, don’t worry too much, as it will come back.
The battery polarization mentioned above will cause lithium precipitation in the electrode and even the formation of lithium dendrites, which will lead to a decrease in battery performance, a reduction in battery capacity, and even safety issues. At this time, the loss is permanent.
Whether it’s temporary or permanent, we certainly want to minimize the damage as much as possible. Automakers are working hard to respond in the following ways:
- Set the preheating battery program before setting off or charging
- Improve energy recovery efficiency
- Optimize the cabin heating system
- Optimize vehicle Battery Management System
- Streamline design of the car body with less resistance
How Cold Weather Affects EV Charging
Just as a suitable temperature is required to convert battery discharge into vehicle kinetic energy, efficient charging also needs to be within a suitable temperature range.
Too high or too low temperatures will increase the resistance of the battery, limit the charging speed, affect the battery performance, reduce the charging efficiency, and cause a longer charging time.
Under low-temperature conditions, the battery monitoring and control functions of the BMS may have errors or even fail, further reducing charging efficiency.
Low-temperature batteries may be unable to be charged in the early stage, which requires heating the batteries to a suitable temperature before charging begins, which is another addition to the charging time.
Plus, many chargers also have limitations in cold weather and cannot provide sufficient current and voltage to meet charging needs. Their internal electronic components also have more suitable operating temperature requirements. Low temperatures may reduce stability and functionality, affecting work efficiency.
Charging cables also seem to be more affected in low temperatures, especially DC charger cables. They are thick and heavy, and coldness may make them stiffer and less bendable making them harder for EV drivers to operate.
Given that many living conditions cannot support the installation of a Private Home Charger, Workersbee’s portable EV charger FLEX CHARGER 2 may be a nice choice.
It can be a travel charger in the trunk but also become a Private Home Charger for electric car owners. It has a stylish and sturdy body, convenient electric charging operation, and flexible high-grade cables, which can provide smart charging up to 7kw. The excellent waterproof and dustproof performance reaches an IP67 protection level, so you don’t have to worry about the performance of safety and reliability even for outdoor use.
If we are convinced that the electric vehicle revolution is right for the future of the environment, climate, energy, and people’s well-being, and even beneficial for the next generation, then even knowing that we will face these cold weather challenges, we should spare no effort to implement it.
Cold weather poses big challenges to the range, charging, and even market penetration of electric vehicles. But Workersbee is sincerely looking forward to working with all the pioneers to discuss the innovation of thermal management technology, the prosperity of the charging environment, and the advancement of various feasible solutions. We believe challenges will be overcome and the road to sustainable electrification will become smoother and broader.
We are honored to discuss and share EV insights with all our partners and pioneers!
Post time: Feb-29-2024